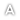Working of Heart
- Details
- Last Updated on Thursday, 25 September 2014 11:17
WORKING OF THE HEART AND ITS BLOOD SUPPLY
Heart is a muscular pump, made up of specialized muscles. The right half of the heart receives impure (deoxygenated) blood from the body and pumps it into the lungs. The left half of the heart receives pure (oxygenated) blood and pumps it to the rest of the body. The left half of the heart is stronger and thicker.
In order to function, the heart needs nourishment. The nourishment comes to the heart via blood which is supplied to the heart through two major coronary arteries : left and right coronary arteries. The left coronary artery again divides into two major branches (left anterior descending and left circumflex arteries), from which several smaller branches arise and supply the heart. Thus, there are three major arteries : left anterior descending artery, left circumflex artery and right coronary artery.
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery(A Guide to Patients)
- Details
- Last Updated on Thursday, 25 September 2014 11:14
Introduction
This web page is for the patients undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG). This web page attempts to explain the cause of the disease, the risk factors, the effects of disease and possible treatment options. It tells about the surgery, preoperative preparation and postoperative care in hospital and at home. Lastly, an effort has been made to spread preventive awareness about the coronary artery disease. For better understanding, at the cost of technical perfection, language has been made as simple as possible.
Anticoagulation
- Details
- Last Updated on Wednesday, 17 September 2014 14:08
Anticoagulation
 |
 |
| Patient ID Card | Patient ID Card |
Oral anticoagulants (Acitrom) is prescribed to prevent blood clot formation on and around the mechanical valve. This drug must be taken carefully and under supervision. If the level of drug is not enough. Blood clot may form on the valve and can clog the valve or can produce a stroke. Excess level of this drug can cause bleeding, both externally and internally.
Your doctor will determine the level of anticoagulant that is right for you. To maintain proper levels of anticoagulation, take your medication as prescribed and follow up with blood tests as scheduled. The dosage will be closely monitored by blood tests. The blood tests include a PT or INR.
Some important points of anticoagulant therapy are:
- Take drug carefully. See the strength of the tablet. Acetrom is available in 1mg, 2mg, 3 mg and 4 mg strength. Preferably take the drug at a fixed time of the day:
- Regular follow-up visit to your doctor.Get your Prothrombin (PT) done at each visit. The INR (International Normalized Ratio) should be between 2 and 4.
- Avoid food rich in Vit-K
- Avoid alcohol
- If you develop some other ailment, inform the treating doctor that you are receiving oral anticoagulants. Some drugs (amiodarone, propranolol, sulfinpyrazone, cotrimazole, ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, isoniazide, metronidazole, fluconazole, aspirin, ibuprofen, cimetidine, omeprazole, tamoxifen, danazole etc.) increase the effect of Acitrom while other (rifampicin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, sucralfate etc) decrease its effect. Thus dosage adjustment may be required.
- Inform the doctor if you develop any of the following:
- Excessive menstrual bleeding
- Blood mixed urine
- Bloody or black, tarry stools
- Unusual nosebleeds
- Bleeding gums
- New onset, resistant headache
PREGNANCY
In cases of young female patients, if pregnancy is anticipated in future, it should be discussed with the cardiac surgeon, even before surgery. If pregnancy is anticipated, valve repair, bioprosthesis, homografts or autografts are preferred options because use of oral anticoagulants during pregnancy may cause neurological or skeletal/facial abnormalities in the fetus. Also it may increase the chances of fetal loss and bleeding at the time of child birth.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR FEMALE PATIENTS RECEIVING ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS
- No unplanned, unsupervised pregnancy. Inform the doctor if you have become pregnant or are planning to become pregnant.
- Plan hospital delivery only.
- Regular check-up during pregnancy
- Hospitalization 2 weeks before the date of delivery. In hospital, oral anticoagulants are stopped and Heparin is started which is continued for one week after delivery.
- Inform your doctor urgently, if you develop any of the following:
Anticoagulation related bleeding
·- Valve Thrombosis: The valve clicks usually decrease in intensity or disappear. Patient develops new onset shortness of breath and effort- intolerance.
- Thromboembolism:Blood clot from the valve may go to the brain or any of the limbs. If clotreaches to brain, the patient may develop stroke.If it reaches to one of the limbs, there is sharp pain in the limb and the limb becomes cold.
- Prosthetic valve Endocarditis:Infection of the heart valve manifests as prolong, resistant fever,anaemia and sometimes smoky urine.
Parts of the Heart
- Details
- Last Updated on Wednesday, 17 September 2014 14:08
Parts of the Heart
The heart acts as a pump. It is divided in to a right and left portion. The right portion receives blood (which is impure) from the body and pumps the same to the lungs for purification (oxygenation). The impure blood enters the heart from two large veins called the superior and inferior vena cava. The blood from these veins enters the right upper chamber known as the Right Atrium. This chamber also receives impure blood from the heart veins through the coronary sinus. The right atrium pumps this blood into the Right Ventricle or the right lower chamber through the Tricuspid Valve. The tricuspid valve prevents blood from flowing from the right ventricle to the right atrium. The right ventricle pumps blood into the Pulmonary Artery. The Pulmonary Valve prevents blood from leaking back into the right ventricle. The pulmonary artery carries impure blood to the right and left lungs. The left half of the heart collects and pumps pure (oxygenated) blood from the lungs to all parts of the body. The blood from the lungs enters the heart from four veins called the Pulmonary Veins. These veins bring the blood into the left upper chamber called the Left Atrium. The left atrium pumps blood through the Mitral Valve into the left ventricle or left lower chamber.
The mitral valve prevents blood from leaking back from the left ventricle to the left atrium. The left ventricle pumps the blood into the Aorta, which circulates to all parts of the body. The Aortic Valve prevents blood from leaking back into the left ventricle. The four valves in the heart are the Mitral and Aortic valves on the left side and Tricuspid and Pulmonary valves on the right side.
Care for Patients
- Details
- Last Updated on Wednesday, 17 September 2014 14:09
Special Precautions of Care for Patients with Mechanical Heart Valves
GENERAL
- Make regular visits to your doctor. It is essential for proper regulation of your medicines.
- Proper dental hygiene is very important. Infection from teeth may involve your valve.
- Treat all minor infections vigorously. Consult the local doctor for skin infections, respiratory tract, urinary tract or similar infections.
- Avoid hazardous life-style. Your wounds will bleed excessively. In case of minor cuts or abrasion, prolong pressure is required to stop the bleeding.
- Take medicines carefully. ‘Do not practice self medication’ Do not take drugs, especially pain killers without the advice of a doctor. In case of an ailment, inform the doctor that you are taking oral anticoagulants.
- For all minor surgical procedures, you need hospitalization and switching over from oral anticoagulants to heparin. All such minor procedures should be performed under antibiotic cover.
- All patients who have rheumatic heart disease, require Penicillin therapy till the age of 45 years. Always receive penicillin injection with disposable syringe and needle. In case of allergy to penicillins, inform your doctor.
- Carry an identify card with you which, in case of emergency, may inform the hospital personnel that you have undergone a valve replacement and that you are receiving oral anticoagulants.
- Stop smoking. Alcohol may affect the level of anticoagulation, better avoid it.
- Avoid diet which is rich in Vitamin K. (spinach (palak), cabbage(Patta Gobhi), lettuce, broccoli(Green-Gobhi), cauliflower(Phool-Gobhi), tomatoes(Tamatar), carrots(Gajar), butter(Makhan), olive(Jaitun ) or corn oil and eggs(Anda)).
More Articles...
- Heart Valve Surgery (A Guide to Patients)
- PAST RESULTS
- Result Notification to the M.Sc. courses for August 2007 on the basis of their performance in the Entrance Examination held on 7th July, 2007.
- Result Notification to the M. Biotechnology course for August 2007 session on the basis of their performance in the Entrance Examination held on 21st July, 2007
Subcategories
Contact Us
All India Institute of Medical Sciences
Ansari Nagar, New Delhi - 110029
Board Number : +91-11-26588500 / 26588700
Fax : +91-11-26588663 / 26588641